
28 Mar What is an ISO 6 Cleanroom? A Guide for Beginners
ISO 6 cleanrooms play an important role in many industries. While all cleanrooms control the number and size of particles, the specific limits vary by ISO class. In this guide, we’ll go over what ISO Class 6 cleanrooms are and how they are used.
What is an ISO 6 Cleanroom?
An ISO 6 cleanroom, as defined by ISO 14644-1 standards, is a controlled environment that limits the number and size of airborne particles, allowing no more than 35,200 particles (0.5 micrometers or larger) per cubic meter. These cleanrooms require 150 to 240 air changes per hour and generally use turbulent airflow. They are considered mid-range within the ISO classification system.
Specifically, they permit a maximum of each per cubic meter:
- 1,000,000 particles of 0.1 micrometers or larger
- 237,000 particles of 0.2 micrometers or larger
- 102,000 particles of 0.3 micrometers or larger
- 35,200 particles of 0.5 micrometers or larger
- 8,320 particles of 1 micrometer or larger
- 293 particles of 5 micrometers or larger
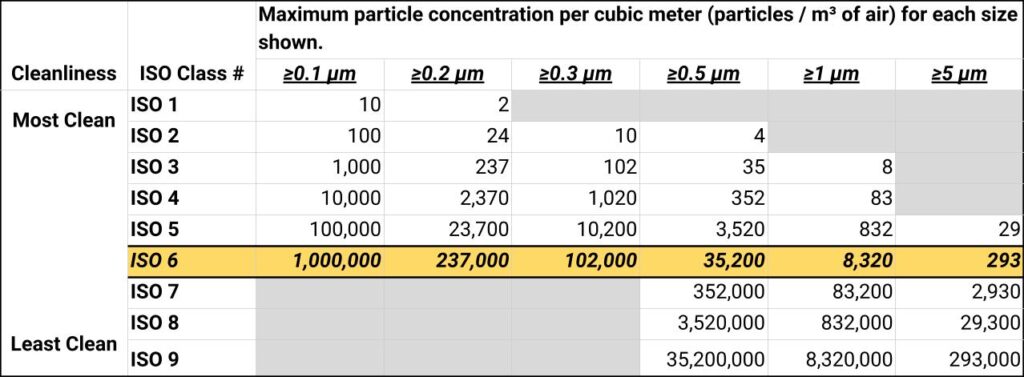
Unlike ISO 7 cleanrooms, they include limits on particles that are 0.1, 0.2, and 0.3 micrometers or larger per cubic meter. On the whole, this means they are more strict and allow fewer particles than ISO 7–9 cleanrooms.
Is an ISO Class 6 Cleanroom the Same as a Class 1,000 Cleanroom?
ISO Class 6 cleanrooms are equivalent to the Class 1,000 category under the outdated Federal Standard 209E, which measured particles per cubic feet. The ISO 14644-1 standard, which uses particles per cubic meter, has since superseded it.
That being said, people still use “ISO Class 6” and “Class 1,000” interchangeably for ease of reference.
How Do ISO 6 Cleanrooms Maintain Air Quality?
The lower the ISO class number, the harder it is to keep the air in cleanrooms clean. ISO Class 6 cleanrooms are considered mid-range, which means that they use some elements that the “cleanest” cleanrooms use, and also some elements that the “dirtiest” cleanrooms use.

Air Changes Per Hour
These environments typically require a high number of air changes per hour (ACPH). The ACPH for them is usually around 180. This means that air is completely recycled in the room three times every minute.
According to The Engineering Toolbox, residential spaces usually have around one or two ACPH, so using a conservative estimate, we could say that the air in ISO 6 cleanrooms is roughly 90 times fresher than the average residential space!
HEPA/ULPA Filtration
Additionally, they use high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filtration to reach and maintain proper particle limits. HEPA filters can stop 99.97% of particles 0.3 micrometers or larger, and they are much better at removing particles than the air systems used in a typical office environment. In some designs, ultra-low particulate air (ULPA) filters might be used, which can screen particles down to 0.12 micrometers.
These filters are typically installed right at the point where clean air enters the room (to minimize contamination from air supply ducts).
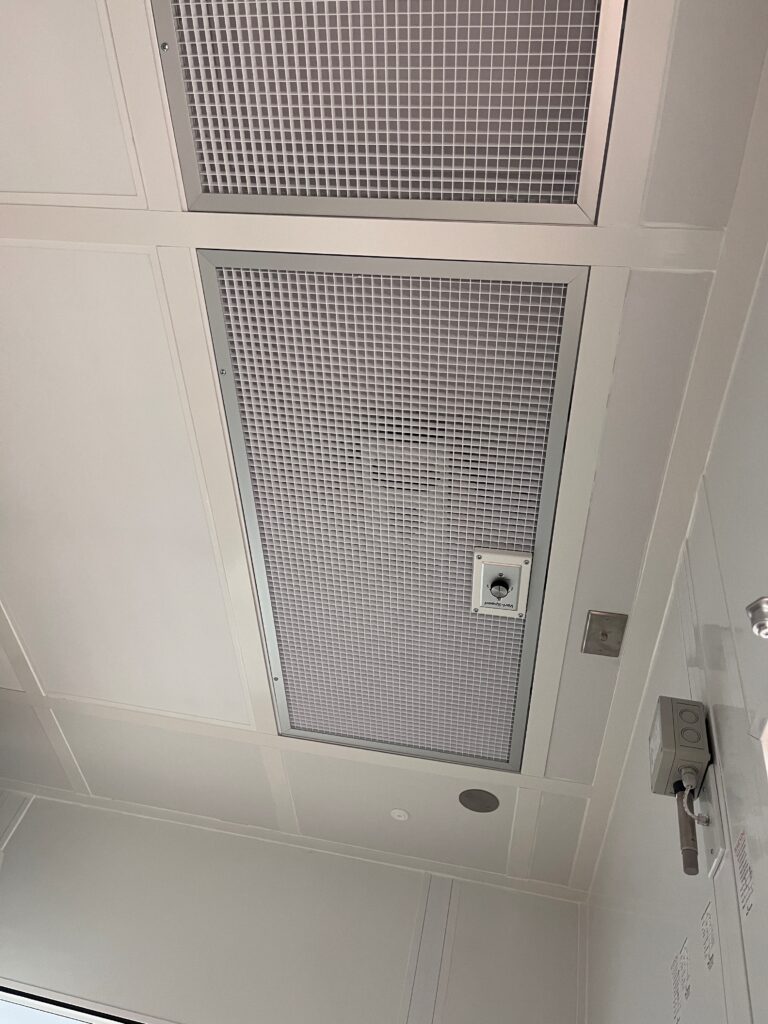

Airflow
Regarding airflow requirements, turbulent flow is generally sufficient to achieve the right particle levels. This means that the air does not need to flow in any specific direction (whether horizontal or vertical), and therefore flows “turbulently” or “randomly.” In some cleanrooms, you may need to use unidirectional or laminar airflow, but this is more rare for ISO 6. The specifics of design features always depend on the application of the cleanroom.
Similarly, in many cases, recirculating airflow systems are used, where the air is continuously cleaned by passing through HEPA or ULPA filters multiple times per hour.
Applications
Furthermore, these environments have various applications and are used in many different industries.
In nanotechnology, for instance, they are essential, as they prevent the contamination of sensitive parts at nanoscale. For parts this small to function, they must be clean of tiny particles, which can cause serious issues to components and products.
Here are a few other industries that commonly use them:
- Semiconductor and electronics manufacturing
- Pharmaceutical compounding and production
- Biotechnology research and production
- Advanced medical device manufacturing
- Optical manufacturing
- Cleantech
- Aerospace
These cleanrooms ensure the controlled conditions necessary in industries where the highest standards of cleanliness are a prerequisite for success.
Customizing ISO 6 Cleanrooms
For a tailored cleanroom design that meets your specific industry and operational needs, consider consulting with the experts. At Allied Cleanrooms, our engineers are ready to guide you through the customization process, ensuring your cleanroom perfectly aligns with your requirements. Contact us today to start designing your ideal cleanroom solution.

