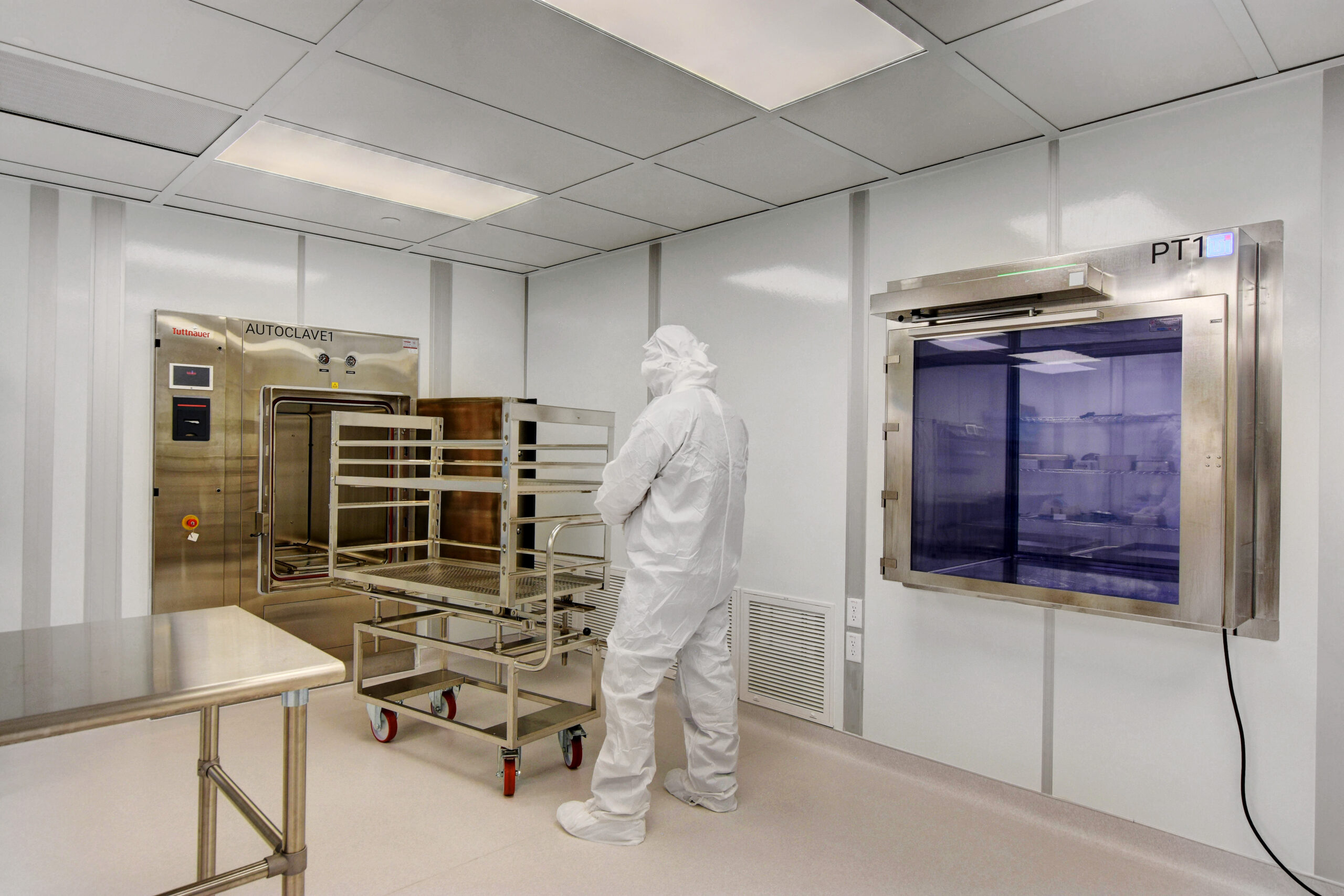

21 Mar What is an ISO 7 Cleanroom? What You Need to Know
Understanding cleanrooms and their ISO classifications can be confusing. Simply put, cleanrooms limit airborne particles in order to prevent contamination. Each ISO class only differs in the number and size of particles allowed. In this guide, we’ll specifically focus on ISO 7 cleanrooms and their features, requirements, applications, and more.
What is an ISO 7 Cleanroom?
An ISO 7 cleanroom, as defined by ISO 14644-1 standards, is a controlled environment that limits airborne particles to no more than 352,000 particles (0.5 micrometers or larger) per cubic meter. These cleanrooms require 60 to 90 air changes per hour and can use a combination of unidirectional and non-unidirectional airflow. They are commonly used in industries such as pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and electronics manufacturing.
Per cubic meter, they allow a maximum of the following:
- 352,000 particles for sizes 0.5 micrometers or larger
- 83,200 particles for sizes 1 micrometer or larger
- 2,930 particles for sizes 5 micrometers or larger
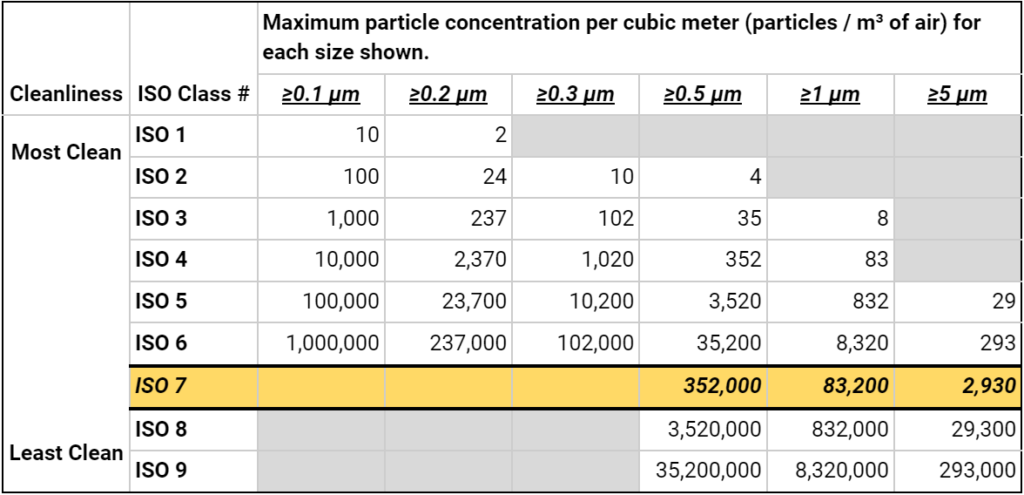
As you can see from the chart above, ISO Class 7 cleanrooms only target particles that are 0.5 micrometers or bigger. They do not focus on smaller particles, such as those between 0.1 and 0.3 micrometers. This is because, in general, smaller particles have less impact on the work done in these rooms. ISO classifications are selected based on the sizes of particles that cause the most trouble.
Are ISO Class 7 Cleanrooms the Same as Class 10,000 Cleanrooms?
ISO 7 cleanrooms directly correspond to Class 10,000 under the older Federal Standard 209E. This older standard used particles per cubic feet for measurement. The ISO 14644-1 standard, on the other hand, uses particles per cubic meter, and has replaced Fed Standard 209E.
Although the Federal Standard 209E is no longer in use, the terms “Class 10,000,” “Class 1,000,” etc., are still commonly used for ease of reference.
Both ISO 7 and Class 10,000 cleanrooms allow less than 352,000 particles bigger than 0.5 micrometers in each cubic meter of air, so we can say that they are the equivalent, or the same.
ISO 7 Cleanroom Requirements
To keep particles below required levels, these cleanrooms have special requirements. They achieve this by frequently changing the air, using efficient filters, and managing airflow. In this section, we’ll cover key requirements such as air changes per hour, HEPA filtration, and airflow control.

Air Changes per Hour
A high number of air changes per hour (ACPH) helps cleanrooms stay clean. This metric tells us how often the air in a room is completely changed with new air in one hour.
In ISO 7 cleanrooms, the air is replaced 60 times each hour. This means that every minute, the air inside is entirely renewed.
For some perspective, the American Society of Heating, Refrigerating, and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE) suggests that a typical home should have a minimum of 0.35 ACPH to ensure good indoor air quality.
In other words, these cleanrooms are significantly cleaner than a typical house.
HEPA Filtration
A high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filtration system is necessary for filtering out particles in an ISO 7 cleanroom.
These filters are highly efficient, trapping 99.97% of particles 0.3 micrometers or larger. As a result, they are able to capture almost all airborne particles of this size and larger.
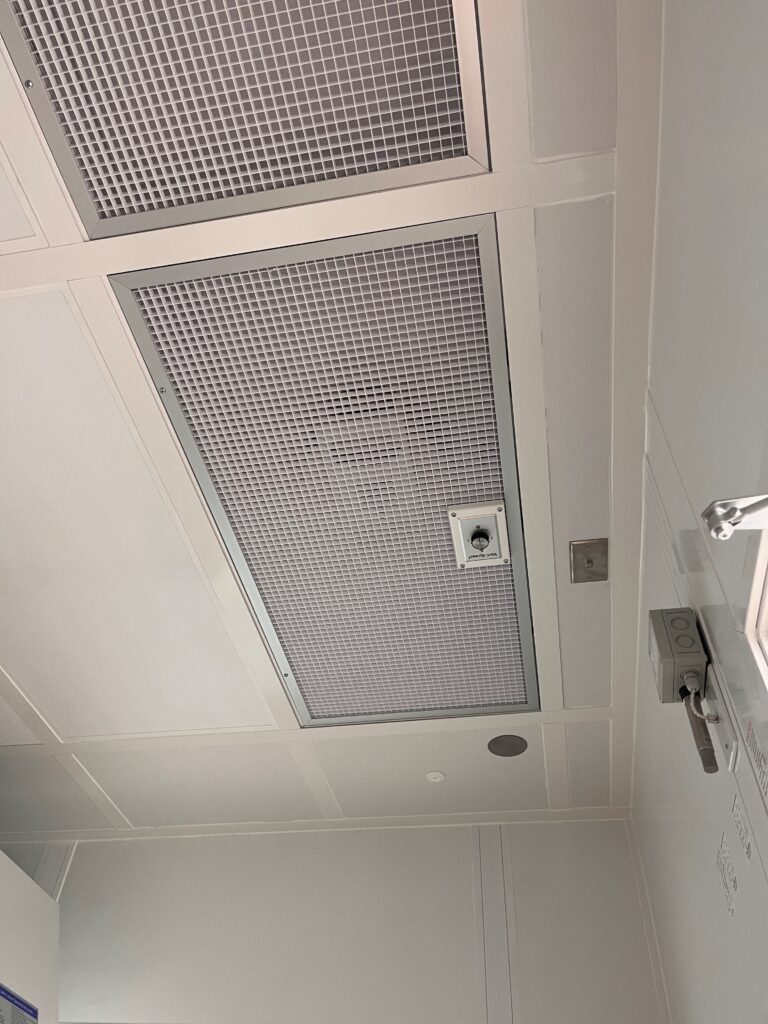

Airflow Control
In ISO Class 7 cleanrooms, how airflow is designed is just as important as filtration.
In most cases, turbulent air flow is sufficient to meet the standard. However, in special cases, you may need unidirectional or laminar flow, where air moves in a single direction at a consistent speed.
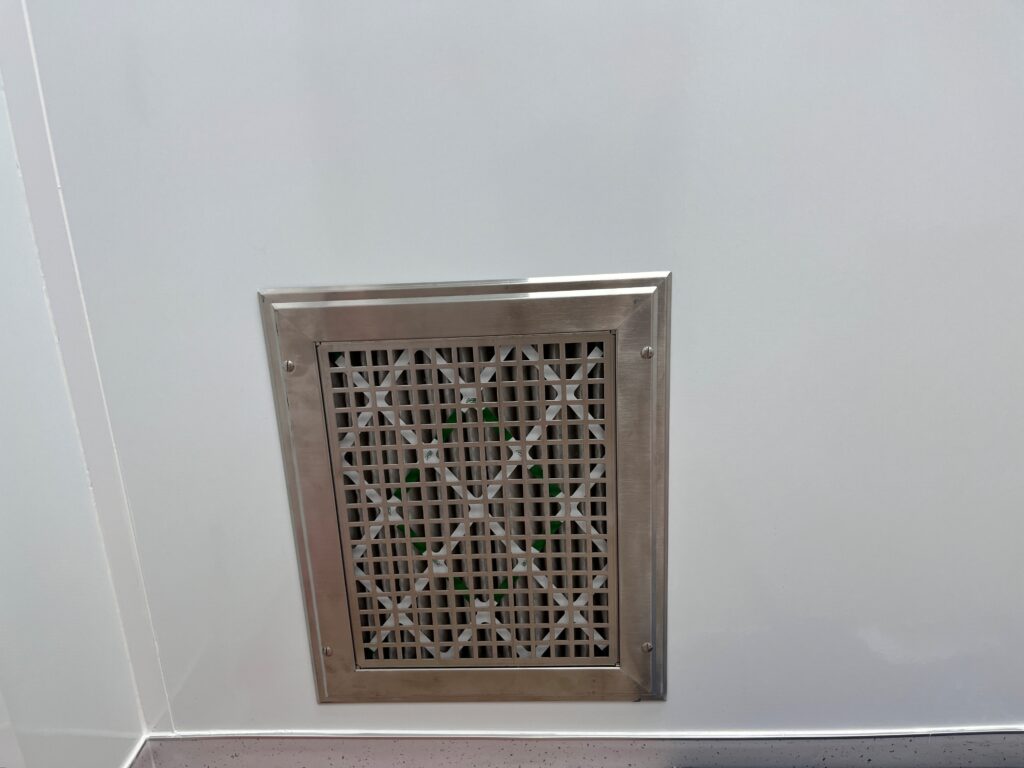

Unidirectional airflow sweeps particles away from critical areas towards air returns in the lower walls or floor, preventing turbulence that may push particles back into the air.
The combination of HEPA filtration and carefully designed airflow patterns minimizes the overall risk of contamination in sensitive areas.
What are Some Applications of ISO 7 Cleanrooms?
These cleanrooms are used in many sectors and are important for both making safe products and meeting regulations.
For example, in making medicines, they stop contamination during important steps like product filling. These cleanrooms also serve in the production of sterile drugs, the construction of spacecraft parts, and the preparation of food.
Other industries that commonly use these cleanrooms include:
- Biotechnology
- Electronics
- Optical manufacturing
- Medical devices manufacturing
- Automotive manufacturing

Understanding ISO 7 Cleanroom Variability
While ISO 7 cleanrooms are designed to meet strict standards, factors such as size, layout, specific industry requirements, and individual customer needs can greatly influence their design. Given these differences, it’s important to customize each cleanroom for its intended use.
If you’re considering an ISO 7 cleanroom, we recommend contacting our engineers at Allied Cleanrooms. They can guide you through the options and help design a cleanroom that perfectly fits your requirements.

