
29 Apr Cleanroom Certification
Cleanroom certification is a process that verifies whether a cleanroom meets proper standards, such as the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) or other benchmarks, and is done mainly through testing. Some testing procedures are required for all cleanrooms, and others are only required in certain industries. Cleanroom testing and certification is done by a third party, but testing is also recommended internally.
1. Classification Standards
The sizes and counts of airborne particles are used to categorize cleanrooms. The primary requirements include:
- ISO 14644-1: This standard classifies air cleanliness levels by measuring particle concentration per cubic meter.
- FED STD 209E: Though this standard has been replaced by ISO, it still remains relevant in some contexts, and measures air particles per cubic foot.
Both of these standards are related as follows:
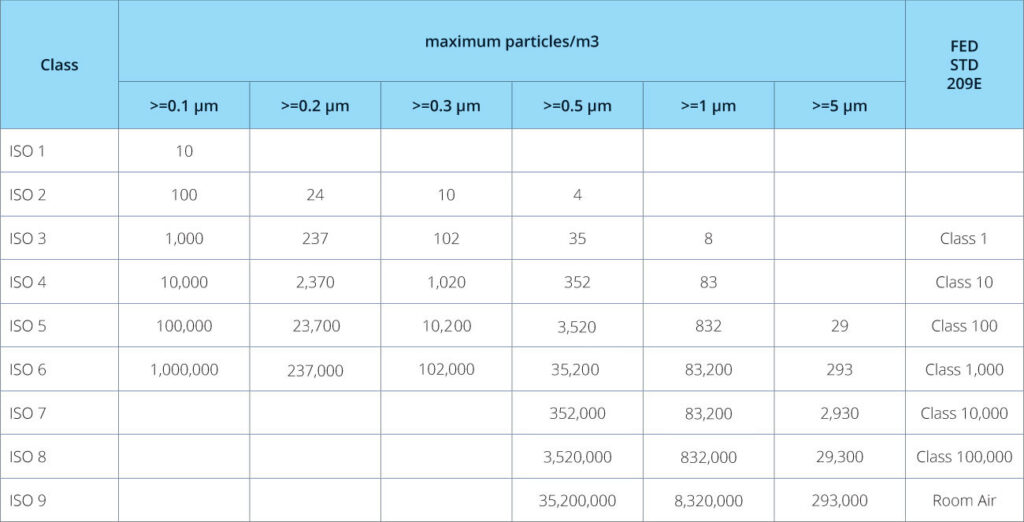
Industry-specific standards include:
- USP Chapter <797> and <800> for pharmaceutical compounding environments.
- ISO 13485 for medical devices, covering quality management systems.
- ASTM E2352 for aerospace, standardizing cleanroom operations.
- Institute of Environmental Sciences and Technologies (IEST).
- Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and Current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMP).
2. Testing Procedures
Cleanroom certification often involves:
- Airflow Tests: to check that air movement does not prevent particles from lingering.
- Particle Counts and Viable Particle Counting: to ensure particle concentration does not exceed the class limits.
- Tests for Air Change Rates and Airflow Volume Velocity: to check for sufficient air turnover/replacement.
- Temperature/Relative Humidity Measurement: to confirm whether HVAC controls are functioning properly.
- HEPA Filter Testing and ULPA Filter Testing: to ensure HEPA filter integrity and also make sure HEPA filtered air continues to trap the right particle sizes.
- Pressure Differential Testing for room pressure: to check necessary pressure differences that keep contaminants out (or in).

3. Advanced Testing
Cleanroom certification might also involve:
- Air Balancing and Visualization: to ensure uniform airflow, often using visual tests.
- Environmental Monitoring: to check air and surfaces for biological contamination.
- Compressed Air Testing: to verify that compressed air systems are contaminant-free.
4. Maintenance
Routine testing is important to keep up with cleanroom standards. Specifically, conduct third-party evaluations and testing and certification services at least once annually, and perform internal evaluations at least once quarterly.
5. Practical Applications
Manufacturing in industries such as pharmaceuticals, aerospace, and semiconductors depends on strict environmental conditions. For example, semiconductor manufacturing cannot tolerate even the slightest particle contamination. Similarly, in aerospace, small particles can cause catastrophic malfunctions in components. As a result, these industries may require stricter-than-usual testing and monitoring.
The Bottom Line
In summary, cleanroom testing and certification is necessary for all cleanroom applications. It helps organizations fight contamination, which in some industries may cause serious issues with products. Standards must continue to keep pace with technological changes to protect economic and scientific outcomes.
Ready to ensure your cleanroom meets the highest standards? Allied Cleanrooms offers customized solutions to fit your needs. Get a free quote today and take the first step towards quality cleanroom performance.

FAQs
What is cleanroom certification?
Cleanroom certification is a process that ensures a cleanroom meets specific standards, such as ISO, through various testing procedures.
Why is cleanroom certification important?
It helps prevent contamination, ensuring product safety and quality, which is crucial in industries like pharmaceuticals and aerospace.
What are the key standards for cleanroom classification?
The primary standards include ISO 14644-1, FED STD 209E, USP Chapter <797> and <800>, ISO 13485, and ASTM E2352.
How often should cleanroom testing be conducted?
Conduct third-party evaluations annually and perform internal evaluations quarterly.
What industries require cleanroom certification?
Industries such as pharmaceuticals, aerospace, semiconductors, and medical devices require strict cleanroom certification.
What are the main testing procedures for cleanrooms?
Key procedures include airflow tests, particle counts, air change rates, temperature/relative humidity measurement, HEPA filter integrity, and pressure differential testing.

